System Design Interview Prep - How to Build a System to Handle Long Running Job
How do you design a Youtube or a Netflix? Have you ever wondered how to build a system that handle long running task like uploading and processing videos to platform like Youtbue or Netflix. Unlike most of the transactions you see in normal websites, these video process takes minutes to hours to finish. What software components you will need? What design pattern will you apply?
The problem
In terms of workload, it can be categorized as long running and short running. For those load that consumes little compute power and get the result soon, it is easy to provide nice user experience since the users will not need to wait for long time. The application can simply request and wait synchrously for the response. The the UI can render properly based on the returned results. This type of system design is simple request-response with consideration of timeout scenario.
However, for those systems that involved expensive workload, like video processing which is IO intensive, you will need different system design so that the long computing workload will run in the background. With this design, your users will not be blocked and continue to use your system’s other features until they get notified the background job is done.
Such workload are usually IO intensive, network bound, or heavy analytical query based on big datasets. Examples could be uploading a video to YouTube processing the vidoes for different resolution for Youtube. The system should allow users to submit a job (alongside with data) and run the task in the background. The end user can continue to use the app. The user will later get notification from email or other channels when the upload is done.
There are a few patterns you can use when designing such system.
Producer Consumer with Queue
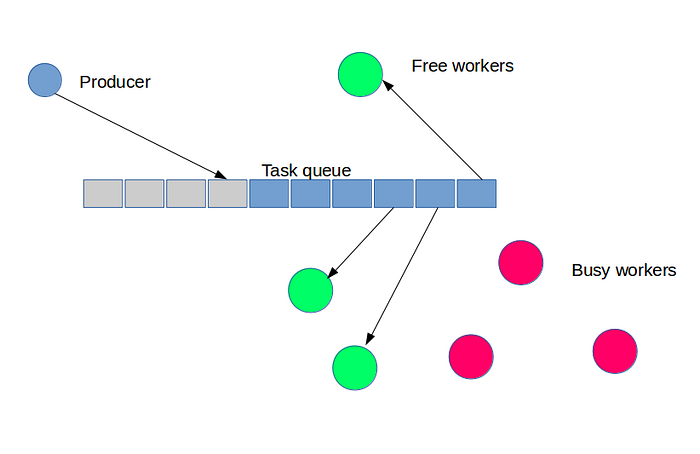
To handle the job asynchrously in the background, we can use a task queue to decouple the producer and consumer. For example, you can create a task queue where a number of workers constantly query for jobs to run. And producer can drop a task then return the control back to the user. In the context of web application with REST API. The API controller would be a producer who encapsulate a task as data payload for the queue. It then drop the task in to a queue. A pool of free workers will grab and execute the job in the background. The instant response of API could be with HTTP Status Code 202. 202 Accepted response status code indicates that the request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. Later, the system will notify the user of progress.
In this design, producer and consumers are decoupled. The system can be horizontally scalable by added more distributed compute power for running the workers. Technologies you will hear for this design will be Message Queues like ActiveMQ, RabbitMQ. Now, in the world of cloud computing there is AWS SQS service will save you a lot of time configuring and managing the hardware.
State Management
The computing process is long running in the back, but the users would like to know the progress of the task. There are a few strategies to accomplish this.
Polling
The worker can constantly update the progress in persistent data storage like a database. And in the front end, the system could call an API to periodically poll the progress of a task from database. Whenever the state change, the web application can update the UI respectively.
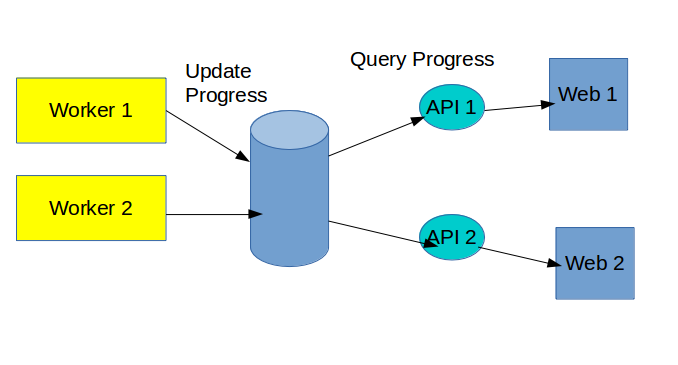
The advantage of this strategy is that it’s easy to implement. But the drawback is that it will waste a lot of bandwith to query if the state does not change for a long time.
Publisher Subscriber with a WebSocket
You can also take advantage of an Open WebSocket and register clients as a subscriber to a certain change events of the task states. The system as a publisher will publish event to the subscribers. In this case, the subscriber will not need to constantly query for state change. In stead, the server will proactively notify the end users.
Some PubSub system allow topic filtering. This feature allows subscribers to retrieve only those events that they are interested in based on the event message.
Error Handling
Error handling is no doubt a critical factor of this system. When an error occurs during computation, the worker can simply return the task to the queue, and let the other workers pick up and retry later. This is quite simple. In AWS SQS, you can define how many time of the queue message can be retried. If there are too many retries it may indicate that the task can be problematic and the error could be permanent. Then the system should remove the task from the task queue. In this case, the workers will not waste their capacity to compute the problematic task. In AWS, the developer can create a Dead Letter Queue for that. The system can constantly monitor the number of message in the Dead Letter Queue. If there are too many message in DQL, that could be something is seriously wrong in the system.
Summary
In the industry, it is very common to build a system to handle long running task. To learn more about System Design, you can find more in Grokking System Design and Designing Data-Intensive Applications.
